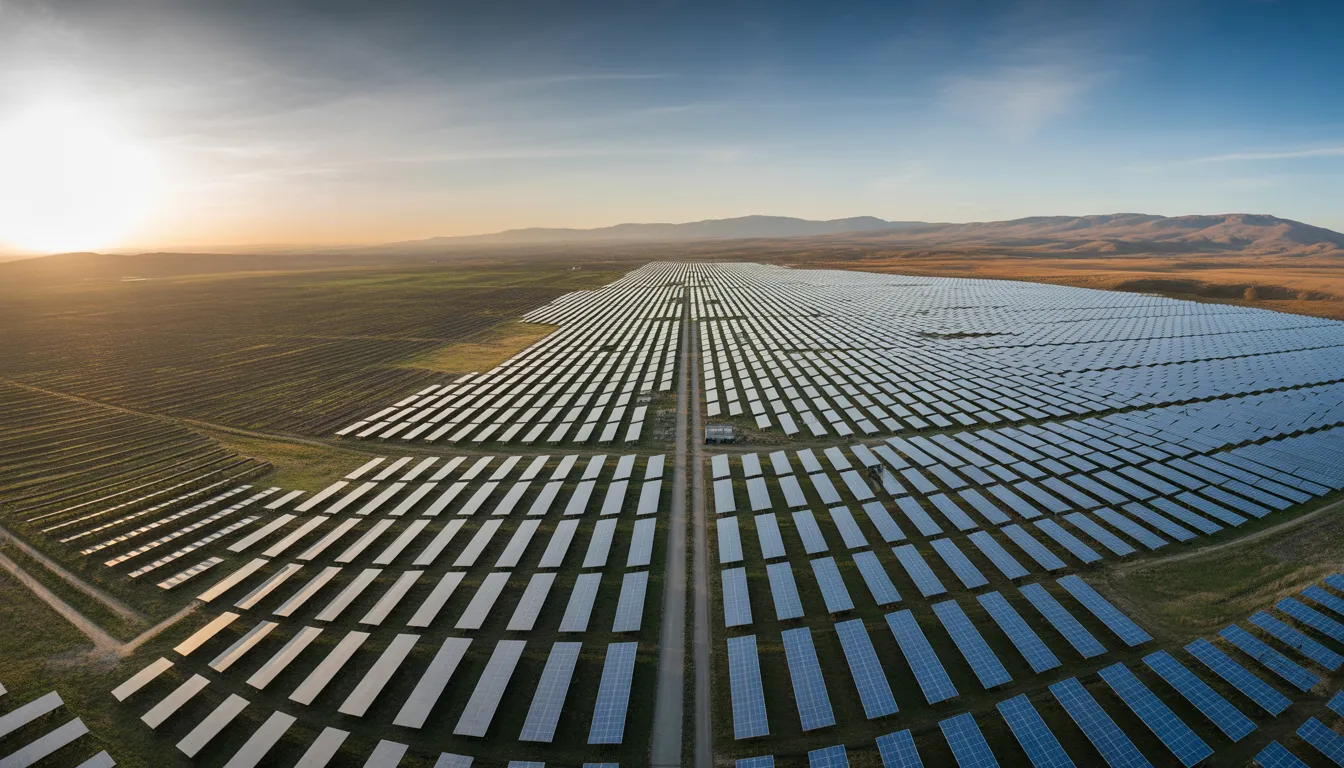
In a groundbreaking study published in Communications Earth & Environment, researchers have developed a pioneering framework that quantifies solar land use with unparalleled precision. This innovative approach, utilizing deep learning and high-resolution aerial imagery, examines 719 utility-scale solar photovoltaic projects in the U.S. Western Interconnection, totaling over 13 GW of capacity. The findings reveal critical insights into land use efficiency, technology selection, and the future of solar energy deployment.
Key Findings and Land Use Efficiency
One of the most striking revelations from this research is the mean land-use efficiency of 24.7 W/m² across the analyzed projects. This metric indicates the amount of power generated per square meter of land, offering a clear benchmark for comparing different solar technologies. Interestingly, the study found that dual-axis solar trackers, which are often lauded for their superior energy yield, actually demonstrate lower efficiency per kW compared to single-axis and fixed-tilt systems. The need for more extensive spacing to avoid shading reduces the land efficiency of dual-axis trackers, challenging previous assumptions about their effectiveness.
Understanding Solar Tracker Technologies
Solar installations typically utilize three types of tracker technologies:
- Fixed-Tilt Systems: Static panels that do not move.
- Single-Axis Trackers: Rotating east-west to follow the sun’s path.
- Dual-Axis Trackers: Adjusting in two dimensions to maximize sunlight capture.
This research highlights that while dual-axis trackers offer higher energy yields, their land requirements make single-axis and fixed-tilt systems more suitable for projects where land efficiency is paramount. This insight is vital for developers and policymakers aiming to maximize solar deployment while minimizing land use impacts.
Historical Land Use and Transformation
The analysis also uncovered that approximately 65% of the solar capacity was installed on developed land, with 38% of sites previously used for agriculture. This shift from cropland to solar energy underscores the necessity for precise metrics to track land transformation. The framework provides a consistent method for evaluating lifetime land transformation, averaging 0.846 m²/MWh, which is crucial for understanding the environmental impacts of solar energy expansion.
Innovative Solutions: Agrivoltaics and Sustainable Siting
A significant opportunity highlighted by the study is the potential of agrivoltaics, which integrates solar energy generation with agricultural practices on former cropland, effectively optimizing land use. Additionally, utilizing brownfields and disturbed sites for solar development aligns with sustainable siting strategies aimed at minimizing new ecological impacts. This framework supports such initiatives by identifying optimal siting opportunities, which are critical as solar energy continues to expand rapidly.
Implications for Policy and Standardized Metrics
The new framework addresses previous inconsistencies in land-use metrics, offering standardized measures for efficiency (W/m²) and land transformation (m²/MWh). This consistency aids lifecycle assessments and informs planning processes, aligning with goals outlined in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 7 for clean energy and SDG 15 for life on land). Furthermore, it highlights that less than 0.5% of vast federal lands might suffice to meet ambitious renewable energy targets, emphasizing the importance of strategic land use in solar energy growth.
Conclusion: A Path Forward for Solar Energy
As the solar industry continues to evolve, this new framework serves as a critical tool for achieving sustainable solar deployment. By providing detailed insights into land use efficiency and technology performance, it empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions that balance energy production with ecological preservation. With the right strategies, including the promotion of agrivoltaics and the optimal selection of solar technologies, the renewable energy sector can significantly contribute to a sustainable future.